
Describe Blockchain technology a revolutionary innovation, has transformed the digital landscape. Initially developed as the underlying structure for Bitcoin, blockchain has evolved, influencing various industries beyond cryptocurrency. This article delves into the intricacies of blockchain technology, exploring its core components, functionality, and potential applications.
What is Blockchain Technology?
Unlike traditional databases, which are centralized, blockchain operates on a decentralized network of nodes. Describe Blockchain technology Each node holds a copy of the entire blockchain, and transactions are recorded in a series of blocks. These blocks are linked together using cryptographic hashes, forming a chain—hence the name “blockchain.”
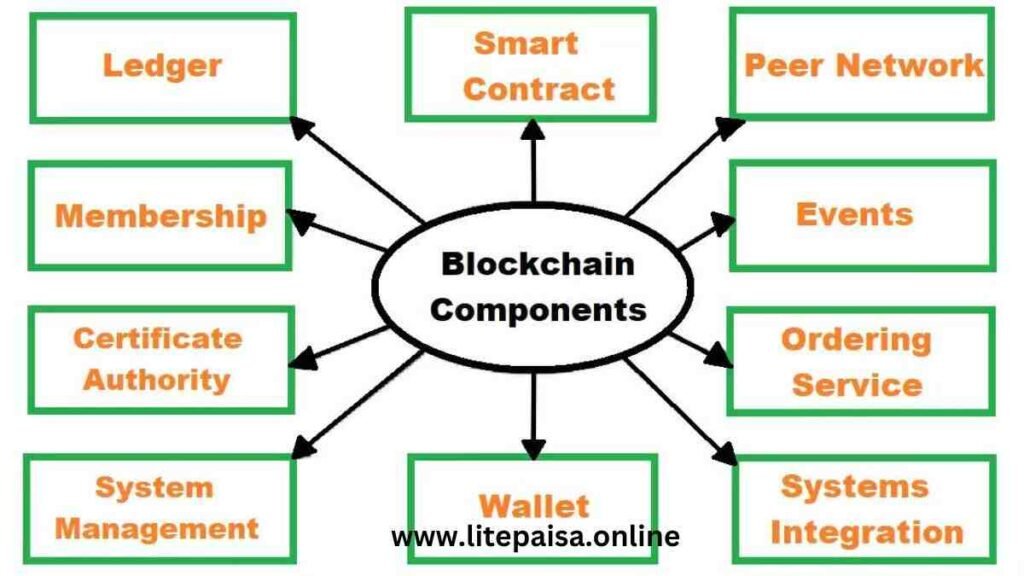
Key Components of Blockchain
Decentralization Describe Blockchain technology
Decentralization is a fundamental aspect of blockchain technology. Instead, all nodes in the network participate in the validation and verification of transactions. This decentralized nature enhances the security and resilience of the blockchain, making it less susceptible to fraud and attacks.
Consensus Mechanisms
Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) are the most commonly used consensus mechanisms.
- Proof of Work (PoW): In PoW, miners solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and add new blocks to the chain.
Cryptographic hashing is a crucial component of blockchain security. Each block contains a unique hash, which is generated using the data within the block. This hash acts as a digital fingerprint, ensuring the integrity of the data. Any alteration in the block’s data results in a completely different hash, making tampering easily detectable.
Smart Contracts Describe Blockchain technology
Smart contracts eliminate the need for intermediaries, reducing costs and increasing efficiency in various applications, such as supply chain management and financial services.
How Blockchain Works Describe Blockchain technology
Transaction Initiation
This transaction is then broadcasted to the network of nodes for validation.
Validation and Consensus
The network of nodes validates the transaction using the consensus mechanism. Once validated, the transaction is grouped with other transactions into a block.
Block Addition Describe Blockchain technology
Each block contains a timestamp, a list of transactions, and a reference to the previous block’s hash, ensuring continuity and security.
Immutability
This immutability ensures that the data on the blockchain remains secure and tamper-proof.
Applications of Blockchain Technology

Cryptocurrency
It provides a secure and transparent method for conducting digital transactions without the need for intermediaries.
Supply Chain Management
Each stage of the supply chain can be recorded on the blockchain, ensuring transparency and reducing the risk of fraud.
Healthcare Describe Blockchain technology
In healthcare, blockchain technology can secure patient records, ensuring data privacy and integrity. It enables seamless sharing of medical information across different healthcare providers, improving patient care and coordination.
Finance
The financial industry benefits from blockchain through faster and more secure transactions. Blockchain can streamline processes such as cross-border payments, reducing costs and increasing efficiency.
Advantages of Describe Blockchain technology Transparency
Blockchain’s decentralized nature ensures that all transactions are transparent and verifiable. Every participant in the network has access to the same data, reducing the risk of fraud and corruption.
Voting Systems
Describe Blockchain technology By recording votes on a blockchain, it ensures that the votes are immutable and verifiable, reducing the risk of electoral fraud.
Real Estate
Blockchain technology can simplify real estate transactions by providing a transparent and immutable record of property ownership. Smart contracts can automate and enforce the terms of real estate agreements, reducing the need for intermediaries.
Security
The use of consensus mechanisms further enhances the security of the network.
Efficiency
By eliminating intermediaries and automating processes through smart contracts, blockchain technology increases efficiency and reduces costs.
Traceability Describe Blockchain technology
Blockchain provides a transparent and traceable record of transactions. This traceability is particularly beneficial in supply chain management, where it is crucial to track the movement of goods and verify their authenticity.
Challenges and Future of Blockchain Technology

Scalability
One of the major challenges facing blockchain technology is scalability. As the number of transactions increases, the blockchain can become congested, leading to slower transaction times and higher fees. Solutions such as sharding and layer 2 scaling are being developed to address these issues.
Regulation
The regulatory landscape for blockchain technology is still evolving. Governments and regulatory bodies are working to establish frameworks that balance innovation with security and compliance.
Interoperability Describe Blockchain technology
Interoperability between different blockchain networks is essential for widespread adoption. Efforts are underway to develop protocols and standards that enable seamless communication between various blockchain platforms.
Adoption
While it holds significant promise, widespread adoption will require overcoming technical, regulatory, and societal challenges.
Blockchain Use Cases Across Various Industries
Banking and Financial Services
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize the banking and financial services industry by offering secure, transparent, and efficient transaction methods. Key applications include:
- Cross-Border Payments: Traditional cross-border payments can take days to process and involve high fees. Blockchain can streamline these payments, making them faster and more cost-effective.
- Fraud Reduction: Blockchain’s immutable ledger reduces the risk of fraud, as all transactions are transparent and traceable.
- Smart Contracts: Automating financial agreements through smart contracts can eliminate the need for intermediaries, reducing transaction costs and increasing efficiency.
Insurance
In the insurance industry, blockchain can enhance transparency and trust between parties. Applications include:
- Claims Processing: Smart contracts can automate and streamline the claims process, ensuring quick and accurate payouts.
- Fraud Detection: Blockchain’s transparent ledger can help in detecting and preventing fraudulent claims.
- Policy Management: Blockchain can simplify policy management by maintaining a single source of truth, ensuring all parties have access to the same information.
Energy Sector Describe Blockchain technology
The energy sector can benefit from blockchain through improved efficiency and transparency in energy trading and management. Use cases include:
- Grid Management: Blockchain can help in managing and optimizing the energy grid by providing real-time data on energy production and consumption.
- Renewable Energy Certificates: Blockchain can streamline the issuance and tracking of renewable energy certificates, ensuring transparency and preventing fraud.
Real Estate
Blockchain technology can transform the real estate industry by simplifying transactions and ensuring transparency. Key applications include:
- Smart Contracts: Real estate agreements can be automated through smart contracts, reducing the need for intermediaries and speeding up the transaction process.
- Title Management: Blockchain can ensure that property titles are accurate and up-to-date, reducing the risk of disputes.
Healthcare Describe Blockchain technology
Blockchain technology can address some of the most pressing challenges in the healthcare industry by improving data security, interoperability, and patient privacy. Use cases include:
- Medical Records Management: Blockchain can provide a secure and immutable record of patient medical histories, ensuring that data is accurate and accessible to authorized healthcare providers.
- Drug Traceability: Blockchain can track the movement of pharmaceuticals through the supply chain, ensuring that drugs are authentic and safe for consumption.
- Clinical Trials: Blockchain can enhance the transparency and integrity of clinical trials by providing a tamper-proof record of data and ensuring that all stakeholders have access to the same information.
Future Prospects of Blockchain Technology

Government and Public Sector
Governments can use blockchain technology to increase transparency, reduce corruption, and improve the delivery of public services. Key applications include:
- Voting Systems: Blockchain can provide a secure and transparent voting system, ensuring the integrity of elections and reducing the risk of fraud.
- Identity Management: Blockchain can provide a secure and tamper-proof system for managing citizen identities, ensuring that personal data is protected.
- Public Records: Blockchain can provide a transparent and immutable record of public records, such as land registries and licenses, reducing the risk of corruption and fraud.
Integration with Emerging Technologies
Blockchain is poised to integrate with other emerging technologies, such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), and Big Data. This integration can unlock new possibilities and drive innovation across various sectors.
- AI and Blockchain: Combining AI with blockchain can enhance decision-making processes and automate complex tasks while ensuring data integrity and transparency.
- IoT and Blockchain: Integrating IoT devices with blockchain can provide a secure and transparent method for managing and analyzing the vast amounts of data generated by IoT devices.
- Big Data and Blockchain: Blockchain can provide a secure and transparent method for storing and analyzing large datasets, ensuring data integrity and privacy.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Describe Blockchain technology
Decentralized Finance, or DeFi, is an emerging sector that leverages blockchain technology to provide financial services without intermediaries. DeFi applications include:
Lending and Borrowing: DeFi platforms allow users to lend and borrow funds without traditional financial institutions, often at lower costs and with greater flexibility.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is a transformative force with the potential to revolutionize various industries by enhancing transparency, security, and efficiency.
Read More: Blockchain Stock Price



